Sejarah Pabrikan Motor Norton
James Lansdowne Norton, lahir di Birmingham pada tahun 1869 dan dibesarkan di sebuah keluarga kelas menengah yang menganut paham religius yang taat. Kemudian saat remaja dia meninggalkan bangku sekolah dan magang ke pembuat sparepart sepeda dan segera terlibat dalam pembuatan rantai sepeda. Pekerjaan tersebut terhenti ketika ia menderita serangan penyakit demam rematik parah ketika ia berusia 19 tahun. Serangan itu begitu buruk sehingga dokter menyarankan bahwa melakukan perjalanan laut merupakan satu langkah terbaik untuk pemulihan kondisi kesehatannya. Anjuran tersebut dilakukannya pada tahun 1888, ia pergi ke New York Amerika dan kembali dengan menggunakan armada kapal new Trans Atlantic liners. Perjalanan laut tersebut cukup membantu mengurangi rasa sakit tetapi ia tetap menderita penyakit tersebut seumur hidupnya. Sejarah berikutnya dimulai pada tahun 1898, ketika ia mendirikan perusahaan Norton Manufacturing Company di Bromsgrove Street, Birmingham. Salah seorang temannya bernama Charles Riley Garrard, seorang pengusaha kaya raya, melihat ada sebuah potensi dan peluang menghasilkan uang dari sektor tranportasi. Pada saat itu Prancis adalah perintisnya, dan pada tahun 1902 Garrard mendapatkan kesepakatan untuk impor mesin buatan Clement France yang akan dipasang ke sepeda dan dipasarkan dengan nama mesin Clement-Garrard.
Perusahaan Norton mendapat order membangun frame untuk Garrard. Dan pada November 1902 sepeda bermesin pertama buatan Norton diproduksi dan diiklankan oleh Norton pada tahun 1903 dengan nama Energette . Dalam iklan tersebut disebutkan sepeda ini sebagai sepeda yang ideal untuk dokter dan cocok untuk bisnis, touring dan balap.
Seperti mesin produksi Clement yang lain, mesin Norton Energette ini bertype 4T 145cc dengan menggunakan Atmospheric intake valve dan Mechanical exhaust valve. Kecepatan maksimal Norton Energette ini kira-kira 20mph (sekitar 32kmh) :D
Selain membuat frame untuk Garrard dan Energette-nya sendiri, Norton juga memulai bisnis komponen. Jelas terlihat bahwa Norton telah memutuskan untuk diversifikasi usaha. Nama Energette yang disematkan pada produk Norton pada November 1903 merupakan petunjuk pertama bahwa mesin yang lebih besar sedang dalam persiapan.
Cerita berlanjut saat digelarnya lomba balap pertama 1907 Isle of Man Tourist Thropy (pertama kali diselenggarakan). Kejuaraan ini menandai titik balik dalam sejarah sepeda motor dunia. Pada saat itu, mesin-mesin buatan Prancis mendominasi sebagian besar kejuaraan balap. Aturan internasional saat itu telah menyebabkan beberapa prototype mesin aneh sedang dikembangkan. Pihak berwenang menolak untuk mengubah peraturan tersebut dan akibatnya beberapa prototype mesin balap yang berbahaya mulai dibuat. (hwaduh!) :shock:
Norton tidak ketinggalan untuk ikut serta dalam kejuaraan yang baru pertama kali dimulai tersebut dengan membuat sepeda motor menggunakan mesin V-Twin 726cc buatan Peugeot bertenaga 5Hp.
Motorcycle: Norton Two-cylinder T.T. Manufacturer: Norton Motors Ltd., Aston,
Birmingham Type: Racing Year: 1907
Engine: Peugeot two-cylinder V, four-stroke, with automatic intake valves and side exhaust valves, mechanically operated. Displacement 726 cc.
Cooling: Air
Transmission: Direct, from engine to rear wheel, with a belt
Power: About 5 h.p.
Maximum speed: About 62.5 m.p.h.
Chassis: Single cradle, tubular, open below. Front, elastic suspension
Brakes: Front, skid
Pada saat akan dimulainya kejuaraan 1907 TT tersebut tidak ada yang memperhitungkan keikutsertaan Norton dengan pembalapnya Rem Fowler. Apalagi Motor buatan Norton tersebut belum pernah dicoba sebelumnya pada lintasan balap. Tapi prediksi sebagai underdog tersebut dimentahkan saat race dimulai. Fowler melaju menjadi yang tercepat pada lap pertama kejuaraan tersebut, akan tetapi pada putaran terakhir terjadi masalah mekanis dan menempatkannya pada posisi ke tiga klasifikasi dibawah Charlie Collier dengan motor Matchless dan Jack Marshall dengan motor Triumph.
Sejarah Race TT mencatat Norton ini sebagai yang sepeda motor tercepat pertama kali dalam perlombaan tersebut! hebat! :D
Perusahaan Norton terus berkembang. Pada tahun 1908 Norton Twin diperbesar kapasitasnya sampai dengan 76 x 80mm dan siap mengikuti kejuaraan TT pada tahun 1908. Dua Norton ikut serta dengan rider Fowler dan FC Perryman. Keduanya gagal untuk menyelesaikan lomba, Perryman kehabisan bahan bakar dan Fowler mengalami kerusakan pada klep yang menjadi renggang
Kegagalan Norton bemesin Peugeot ini cukup mengecewakan Norton. Selanjutnya dia segera mendesain ulang mesin ini dengan improvement nya sendiri dan menjadikannya model single Cylinder sidevalve (with fully mechanical valves) bertenaga 3,5hp. Perubahan ini ternyata banyak diminati oleh konsumen dan model ini sukses dalam ujicoba berbagai kondisi jalan dan ketahanan mesinnya.
Setelah melakukan riset yang mendalam akhirnya pada akhir tahun 1911 Norton memperkenalkan type TT 490cc dengan rangka baru lebih rendah, wheelbase lebih pendek dan dimensi mesin 79x100mm. Ini merupakan saat pertama Norton membuat sepeda motor dengan tujuan balap. model ini mendapat sukses besar dalam kompetisi, menang secara teratur di acara-acara lokal dan nasional.
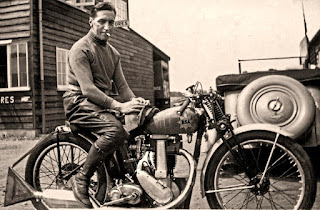
Salah satu kejadian unik terjadi, saat seorang konsumen bernama Jack Emerson (gambar diatas) membeli type TT 490cc. Dia mengendarainya sejauh 165miles dari rumahnya Hull menuju Brooklands. Saat itu dia mampu meraih kecepatan tertinggi dan mengalahkan kecepatan pembalap berpengalaman dengan memecahkan tiga rekor dunia. :shock:
Kabar itu didengar oleh Norton dan segera sepeda motor TT milik Jack Emerson dipinjam dan diteliti oleh Norton. (heran dia) :mrgreen:
Hasil observasi disimpulkan bahwa mesin TT milik Jack Emerson dalam kondisi standar kecuali penggunaan pegas klep memakai yang lebih keras dan kuat. Selain itu penggunaan rasio belt diposisikan untuk menjaga rpm mesin tetap diputaran diatas 3000rpm (catatan : piston masih menggunakan cast iron/besi tuang). Selanjutnya sepeda motor Jack Emerson dikembalikan, dan uniknya saat kembali digunakan menempuh 165miles pada Oktober 1912 sepeda motor ini dapat melampaui kecepatan sepeda motor pembalap Oliver Godfrey (Indian) dan George Stanley (Singer). Hebat!! mesin ini pasti ada
Norton type 16H buatan tahun 1937.
Type 16H diatas sangat populer pada waktu itu. Sampai pada akhirnya terjadilah Perang Dunia II yang menjadi catatan kelam sejarah umat manusia.
Pada saat PDII atau WWII, tidak kurang dari 100.000 unit 16H yang diberi kode “WD” diproduksi untuk keperluan perang.
Type WD 16H ini memiliki bobot lebih berat dari type 16H sebelumnya, penggunaan beberapa bagian komponen menggunakan besi baja tuang dan penambahan bagasi besi menjadikannya bertambah berat. :D
Barisan Norton WD 16H dipakai tentara patroli :shock:
Setelah PDII berakhir, Norton masih tetap memproduksi 16H yang kebanyakan dijual untuk pasar domestik. Banyak konsumen dari warga masyarakat membeli Norton 16H untuk dipasangi sidecar sekedar untuk jalan-jalan bersama keluarga.
Penjualan Norton 16H dengan memakai sidecar ini mulai seret ketika mulai diproduksinya mobil-mobil murah oleh perusahaan otomotif waktu itu.
Pada tahun 1949, type 16H mendapatkan upgrade berupa penggunaan suspensi depan teleskopik.
Kemudian pada tahun 1952 suspensi belakang disematkan pada type 16H dengan model plunger.
Dengan upgrade suspensi tersebut ternyata tidak dapat meningkatkan penjualan. Beberapa model dan seri diproduksi untuk memberikan beberapa pilihan kepada calon konsumen dan menguasai pasar. Akan tetapi kehadiran mobil-mobil murah yang booming waktu itu sangat berdampak pada penurunan penjualan sepeda motor Norton. Tapi Norton Motorcycle masih terus bertahan sampai sekarang dan terus memproduksi sepeda motor dengan produk terbarunya Norton Commando series.
Sekian aja ya sejarah panjang Norton! :mrgreen:
Berikut ini beberapa sepeda motor yang pernah diproduksi Norton yang saya persembahkan untuk penggemar motor lawas :D
Sebenarnya masih banyak seri dan type sepeda motor produksi Norton yang lain. Dan yang terakhir ini special buat bro Arie Slight yang demen sama Norton seri berikut ini! (nanti akan saya coba buat artikel tersendiri) :mrgreen:
1961 Manx special Cafe Racer 500 cc
akan tetapi perjalan bisnis tidak semudah yang dibayangkan, pada
tahun 1913 norton berada diambang kebangkrutan ketika RT Shelley &
Co, kreditur modal utama masuk. Norton Motors Ltd kemudian dibentuk.
Bertempat di Brooklands didirikan pusat dan riset pengujian kecepatan.
RT Shelley & Co dalam hukum adalah ace tuner Dan O’Donovan mesin
baru dikirim bersama untuk dilakukan pengujian oleh dia, dalam Rolling
chassis dikenal sebagai ‘Old Miracle’, pemegang banyak rekor kecepatan
dan sampai sekarang masih disimpan di museum. Mesin yang diuji tidak
untuk dijual sampai diperoleh performa yang tepat. Motor Norton
mendapatkan kontrak dengan pemerintah pada waktu Perang dunia 1 untuk
memasok mesin untuk tentara Rusia pada tahun 1916, dan pabrik norton di
pindah ke tempat yang lebih besar di Bracebridge Street, Aston. Yang
terkenal Norton logo dibuat sekitar waktu ini.
Pada awal 1913, Norton telah merancang mesin dengan katup udara dengan operasi desmodromic, tapi tidak sampai 1922 motor norton menghasilkan mesin OHV pertamanya, Model 18 sebagai salah satu motor norton single tercepat . Pada 1923 Maudes Trophy diperoleh untuk pertama kalinya ketika motor Norton Model 18 memecahkan rekor dunia delapan belas di Brooklands, ditunggangi oleh sebuah tim yang terdiri dari O’Donovan, Bert-tiba dan Nigel pada musim semi. Piala itu terus dipertahankan selama tiga tahun setelah prestasi serupa kecepatan dan daya tahan.
Dengan 1.924 nama model yang akrab lainnya seperti 16H dan Model 19 telah diperkenalkan, yang terakhir versi 588cc Model 18. Mereka juga memiliki OHV prototipe 250cc akan tetapi tidak pernah diproduksi karena tidak memenuhi kriteria pasar pada waktu itu. Alec Bennett memenangkan Balap TT Senior dengan OHV Norton, rata-rata lebih 60mph untuk pertama kalinya.
James Norton meninggal pada 1925 pada usia 56, meskipun penampilan kebapakan di foto dengan rambut perak dengan kacamata berbingkai kawat memberi kesan jauh lebih tua. Dia dihormati di seluruh industri karena kemampuannya rekayasa dan integritas. Sesaat sebelum kematiannya ia telah mengambil liburan panjang di Afrika Selatan atas saran dari dokter dan dari kondisi jalan ia melihat ada ekspor atau model ‘kolonial’ diberi ground clearance yang lebih tinggi bersama dengan berbagai modifikasi yang sesuai lainnya.
Sementara itu, di trek balap Eropa,Motor Norton yang membangun Kekuatan industri mereka yang harus diperhitungkan, memenangkan banyak balapan. Motor Norton memperkenalkan tangki bensin jenis pelana pada mesin balap mereka.type ini menunggu satu atau dua tahun baru diluncurkan, tetapi pada 1926 di London memperkenalkan,Mesin dengan empat gearbox kecepatan dan rem memperluas internal yang berada perlengkapan standar pada beberapa model bersama dengan pelumasan otomatis drive primer rantai. Perusahaan ini secara finansial direkonstruksi sepanjang tahun dan nama berubah menjadi Norton Motors (1926) Ltd Seorang Irlandia muda bernama Stanley Woods memenangkan balap TT 1926 Senior dengan Motor Norton, tetapi untuk tujuan balap mesin pushrod sudah mulai di tinggalkan dan digantikan oleh teknologi baru.
Walter Moore meninggalkan Norton pada tahun 1929 yang pindah ke Produsen NSU di Jerman. Dia secara pribadi memiliki desain mesin OHC sehingga tidak mengherankan ketika NSU mulai memproduksi mesin yang sangat mirip beberapa waktu setelahnya. Motor Norton tidak senang dengan hal ini, setelah merekrut Arthur Carroll untuk mendesain ulang mesin OHC. Motor Norton menghasilkan apa yang menjadi salah satu mesin balap paling dominan sepanjang masa dengan karir berkilauan yang berlangsung selama dua puluh lima tahun ke depan walaupun sesekali ada perlawanan oleh Velocette, Guzzi, Gilera dan BMW.
Norton telah lama menikmati tempat yang
unik dalam sejarah sepeda motor dan terus menarik inspirasi dari masa
lalu sementara membangun warisan Norton untuk masa depan. Nikmati
sejarah yang lebih rinci dari nama Norton sepanjang waktu di bawah ini.
1898 1898
James Lansdowne Norton
(diketahui semua sebagai 'Pa') didirikan
Norton sebagai produsen "fitting dan
komponen untuk perdagangan roda dua."
1900-1910
Pada 1902 sepeda motor
Norton pertama yang diproduksi
menggunakan mesin Perancis dan Swiss. Pada tahun 1907 Rem Fowler
memenangkan Isle of Man kelas silinder
kembar mengendarai Norton, awal tradisi balap yang kuat. Sukses di Isle pertama of Man TT ras, diikuti oleh kemenangan di Brooklands dan ras Eropa lainnya, membantu reputasi semen Norton sebagai pembangun jalan dan ras sepeda serius. 1908 melihat perusahaan ini memproduksi
pertama sepeda Norton bermesin,
didukung oleh unit silinder tunggal sisi
katup dan oleh 1909 Norton sepeda motor yang dijual di Harrods!
1910-1930
Logo Norton yang terkenal, yang dirancang oleh Pa Norton dan putrinya Ethel, muncul di depan katalog 1914 dan dari 1916 Norton dilakukan pada tank mereka. Pada tahun 1925 JL 'Pa' Norton meninggal hanya berusia 56, tetapi tidak sebelum ia melihat sepeda motor itu memenangkan TT Senior dan sespan pada tahun 1924, dengan 500cc Model 18, katup overhead yang pertama Norton tunggal.
1898 1898
James Lansdowne Norton
(diketahui semua sebagai 'Pa') didirikan
Norton sebagai produsen "fitting dan
komponen untuk perdagangan roda dua."
1900-1910
Pada 1902 sepeda motor
Norton pertama yang diproduksi
menggunakan mesin Perancis dan Swiss. Pada tahun 1907 Rem Fowler
memenangkan Isle of Man kelas silinder
kembar mengendarai Norton, awal tradisi balap yang kuat. Sukses di Isle pertama of Man TT ras, diikuti oleh kemenangan di Brooklands dan ras Eropa lainnya, membantu reputasi semen Norton sebagai pembangun jalan dan ras sepeda serius. 1908 melihat perusahaan ini memproduksi
pertama sepeda Norton bermesin,
didukung oleh unit silinder tunggal sisi
katup dan oleh 1909 Norton sepeda motor yang dijual di Harrods!
1910-1930
Logo Norton yang terkenal, yang dirancang oleh Pa Norton dan putrinya Ethel, muncul di depan katalog 1914 dan dari 1916 Norton dilakukan pada tank mereka. Pada tahun 1925 JL 'Pa' Norton meninggal hanya berusia 56, tetapi tidak sebelum ia melihat sepeda motor itu memenangkan TT Senior dan sespan pada tahun 1924, dengan 500cc Model 18, katup overhead yang pertama Norton tunggal.
1930-1950
Pada pertengahan 1930-an
Norton memproduksi lebih dari 4.000
sepeda jalan setiap tahunnya. Antara
perang Norton memenangkan lomba Isle of Man TT Senior sepuluh kali dan, antara tahun 1930 dan 1937, memenangkan 78 dari 92 balapan Grand Prix. Dengan terjadinya perang dunia kedua Norton menarik diri dari balap tapi antara tahun 1937 dan 1945 diproduksi hampir 100.000 sepeda motor sidevalve (hampir seperempat dari semua sepeda motor militer) sebagai kontribusi mereka terhadap upaya perang. Perusahaan menikmati lanjut kemenangan TT setiap
tahun 1947-1954.
1950-1960
1949 melihat pengenalan silinder Dominator kembar, sementara pada tahun 1950 bingkai Featherbed diperkenalkan. Ringan tapi kuat, itu dipasang pada Manx Nortons untuk membantu menegosiasikan putaran Isle of Man track, meningkatkan penanganan sepeda 'dan memberikan kontribusi bagi keberhasilan ras lanjut. Pada tahun 1951 Dominator dan lainnya Norton Cafe Racers yang tersedia dengan
bingkai Featherbed dan keberhasilan
berarti bahwa permintaan untuk frame
yang lebih tradisional dengan cepat
berkurang. Pada akhir musim 1952, Geoff Duke naik untuk Norton, adalah juara dunia baik di 350cc dan 500cc kelas dan dianugerahi OBE.
1960-1980
The 1961 Earls Court motor show digembar-gemborkan pengenalan Commando, dengan unit mesin 'isolastically' terisolasi dari frame untuk kelancaran, getaran-tumpangan gratis. Dalam dekade berikutnya lebih dari 500.000 diproduksivdan dijual dan Commando bernama 'Mesin
Tahun' Sepeda Motor Berita pembaca
selama lima tahun berturut-turut. Pada
1970-an Norton berlari di bawah sponsor dari John Player dan keberhasilan komersial Commando digarisbawahi oleh
kampanye 'Norton Girls'. Namun ini
adalah dekade dimana prevalensi model Jepang melihat Norton, bersama Marques besar Inggris lainnya, dibawa ke ambang kepunahan. The Commando terakhir diproduksi pada tahun 1976.
1980-2000
Pada tahun 1980-an
perusahaan melewati beberapa inkarnasi - hak untuk nama tersebut dibagi antara beberapa perusahaan di beberapa negara. Merek ini diluncurkan di Lichfield pada tahun 1988 dan pada tahun 1989 Norton membuat kembali tegas untuk balap ketika Steve Semprot memenangkan British Superbike Championship pada sepeda JPS hitam-hitam, kemenangan diulang pada tahun 1994 oleh Ian Simpson pada Duckhams Norton. Pasar komersial lebih lambat, meskipun Wankel bermesin Interpol 2 sepeda motor populer dengan pasukan polisi dan RAC. Hal ini menyebabkan penciptaan model sipil disebut Classic. Pada tahun 1992 Steve Hislop, pada ABUS Norton, mengalahkan
Carl Fogarty, mengendarai Yamaha, untuk memenangkan Isle of Man TT Senior, rekaman kemenangan pertama bagi sepeda Inggris selama hampir 30 tahun.
2000-sekarang
Norton pindah ke rumah
saat ini di Donington Park pada tahun
2008 dan pada tahun 2009 CEO Stuart
Garner mengatur Kecepatan Rekor Dunia untuk Rotary Powered Motor (173mph rekaman untuk satu mil waktunya). Pertama Commando 961SE disampaikan pada tahun 2010 dan keberhasilan Commando 961 melihat Norton Motorcycles kembali ke produksi. Pada 2012 Norton kembali untuk balapan TT dengan SG1
dan setelah hasil yang menjanjikan pada tahun 2013, 2014 dan musim masa depan jangka panjang terlihat cerah!
Pada pertengahan 1930-an
Norton memproduksi lebih dari 4.000
sepeda jalan setiap tahunnya. Antara
perang Norton memenangkan lomba Isle of Man TT Senior sepuluh kali dan, antara tahun 1930 dan 1937, memenangkan 78 dari 92 balapan Grand Prix. Dengan terjadinya perang dunia kedua Norton menarik diri dari balap tapi antara tahun 1937 dan 1945 diproduksi hampir 100.000 sepeda motor sidevalve (hampir seperempat dari semua sepeda motor militer) sebagai kontribusi mereka terhadap upaya perang. Perusahaan menikmati lanjut kemenangan TT setiap
tahun 1947-1954.
1950-1960
1949 melihat pengenalan silinder Dominator kembar, sementara pada tahun 1950 bingkai Featherbed diperkenalkan. Ringan tapi kuat, itu dipasang pada Manx Nortons untuk membantu menegosiasikan putaran Isle of Man track, meningkatkan penanganan sepeda 'dan memberikan kontribusi bagi keberhasilan ras lanjut. Pada tahun 1951 Dominator dan lainnya Norton Cafe Racers yang tersedia dengan
bingkai Featherbed dan keberhasilan
berarti bahwa permintaan untuk frame
yang lebih tradisional dengan cepat
berkurang. Pada akhir musim 1952, Geoff Duke naik untuk Norton, adalah juara dunia baik di 350cc dan 500cc kelas dan dianugerahi OBE.
1960-1980
The 1961 Earls Court motor show digembar-gemborkan pengenalan Commando, dengan unit mesin 'isolastically' terisolasi dari frame untuk kelancaran, getaran-tumpangan gratis. Dalam dekade berikutnya lebih dari 500.000 diproduksivdan dijual dan Commando bernama 'Mesin
Tahun' Sepeda Motor Berita pembaca
selama lima tahun berturut-turut. Pada
1970-an Norton berlari di bawah sponsor dari John Player dan keberhasilan komersial Commando digarisbawahi oleh
kampanye 'Norton Girls'. Namun ini
adalah dekade dimana prevalensi model Jepang melihat Norton, bersama Marques besar Inggris lainnya, dibawa ke ambang kepunahan. The Commando terakhir diproduksi pada tahun 1976.
1980-2000
Pada tahun 1980-an
perusahaan melewati beberapa inkarnasi - hak untuk nama tersebut dibagi antara beberapa perusahaan di beberapa negara. Merek ini diluncurkan di Lichfield pada tahun 1988 dan pada tahun 1989 Norton membuat kembali tegas untuk balap ketika Steve Semprot memenangkan British Superbike Championship pada sepeda JPS hitam-hitam, kemenangan diulang pada tahun 1994 oleh Ian Simpson pada Duckhams Norton. Pasar komersial lebih lambat, meskipun Wankel bermesin Interpol 2 sepeda motor populer dengan pasukan polisi dan RAC. Hal ini menyebabkan penciptaan model sipil disebut Classic. Pada tahun 1992 Steve Hislop, pada ABUS Norton, mengalahkan
Carl Fogarty, mengendarai Yamaha, untuk memenangkan Isle of Man TT Senior, rekaman kemenangan pertama bagi sepeda Inggris selama hampir 30 tahun.
2000-sekarang
Norton pindah ke rumah
saat ini di Donington Park pada tahun
2008 dan pada tahun 2009 CEO Stuart
Garner mengatur Kecepatan Rekor Dunia untuk Rotary Powered Motor (173mph rekaman untuk satu mil waktunya). Pertama Commando 961SE disampaikan pada tahun 2010 dan keberhasilan Commando 961 melihat Norton Motorcycles kembali ke produksi. Pada 2012 Norton kembali untuk balapan TT dengan SG1
dan setelah hasil yang menjanjikan pada tahun 2013, 2014 dan musim masa depan jangka panjang terlihat cerah!
English Version
Norton Motorcycle Company
| Industry | Motorcycles |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1898 |
Key people
|
Stuart Garner |
| Website | www.nortonmotorcycles.com |
Wartime WW2 production of the military Model 16 H and Big 4 sidevalve motorcycles was Norton's contribution to the war effort, almost 100,000 being manufactured.
When major shareholders started to leave Norton in 1953, the company declined and Associated Motor Cycles bought the shares.[2] Although motorcycle sales went through a recession in the 1950s, and Norton Motors Ltd was only a small manufacturer, Norton sales flourished. A series of Norton Dominator Twins of 500cc, then 600cc, then 650cc and then the 750cc Norton Atlas kept sales buoyant, especially with sales to the USA.
In 1968, the new 750cc Norton Commando Model appeared, with the engine/gearbox/swingarm unit "isolastically" insulated from the frame with a series of rubber mountings. This kept the vibrations from the rider, giving a smooth comfortable ride. The Commando was a best seller, and voted #1 Motorcycle of the Year a number of times in Britain. 850cc Models appeared for 1973, giving more torque. For 1975 an electric start arrived in the 850 Mk3.
The largest UK motorcycle manufacturer at the time was BSA-Triumph, comprising Birmingham Small Arms Company in Birmingham, and Triumph Motorcycles in Meriden. BSA-Triumph faced difficulties caused by poor management, outdated union practices, old-fashioned motorcycle designs and antiquated factory conditions. A merger with Norton Motorcycles was proposed; but although Dennis Poore's Norton Motorcycles was by far the smaller partner, Poore effectively secured a take-over of BSA-Triumph, forming Norton Villiers Triumph (NVT). The Triumph factory Meriden was the least modern; but workers engaged in a "sit-in", forming a workers' co-operative. Poore was CEO of Manganese Bronze Holdings, a company apparently more concerned with asset stripping than with motorcycle production. Subsequent political manoeuvrings led to the downfall of NVT, as taxpayer-assisted wranglings over amalgamations and sell-offs all but killed the once extensive UK motorcycle industry.
In late 2008, Stuart Garner, a UK businessman, bought the rights to Norton from some US concerns and relaunched Norton in its Midlands home at Donington Park where it will develop the 961cc Norton Commando,[3] and a new range of Norton motorcycles.
The original company was formed by James Lansdowne Norton (known as "Pa") at 320, Bradford Street, Birmingham in 1898.[1] In 1902, Norton began building motorcycles with French and Swiss engines. In 1907, a Norton ridden by Rem Fowler won the twin-cylinder class in the first Isle of Man TT race, beginning a sporting tradition that went on until the 1960s. The first Norton engines were made in 1907, with production models available from 1908. These were the 3.5 hp (490cc) and the 'Big 4' (633cc), beginning a line of side-valve single-cylinder engines which continued with few changes until the late 1950s.[2]
The first Norton logo was a fairly simple, art nouveau design, with the name spelled in capitals.[4] However, a new logo appeared on the front of the catalogue for 1914, which was a joint effort by James Lansdowne Norton and his daughter Ethel. It became known as the "curly N" logo, with only the initial letter as a capital, and was used by the company thereafter, first appearing on actual motorcycles in 1915.[5] Ethel Norton also did some testing of her father's motorcycles.[citation needed]
In 1913 the business declined, and R.T. Shelley & Co., the main creditors, intervened and saved it. Norton Motors Ltd was formed shortly afterwards under joint directorship of James Norton and Bob Shelley. Shelley's brother-in-law was tuner Dan O'Donovan, and he managed to set a significant number of records on the Norton by 1914 when the war broke out - and as competition motorcycling was largely suspended during the hosilities, these records still stood when production restarted after the war.[6] 1914 Dan O'Donovan records set in April 1914 :
- Under 500cc flying km 81.06 mph, flying mile 78.60 mph - 490cc Norton
- Under 750cc flying km and flying mile see above
- Under 500cc with sidecar flying km 65.65 mph, flying mile 62.07 mph - 490cc Norton
- Under 750cc with sidecar flying km and flying mile see above
First World War
Norton continued production of their 3.5 hp and Big 4 singles well into the war period, though in November 1916 the Ministry of Munitions issued an order that no further work on motor cycles or cars would be allowed from November 15, 1916 without a permit.[7] By this time most motor cycle companies were already either producing munitions (or aircraft parts), or devoted to the export trade. Norton were involved in exporting and earlier that year had announced[8] a new 'Colonial Model' of their 633cc Big 4. This featured an increase in ground clearance from 4.25" to 6.5", by altering the frame, larger tank, greater clearance on mudguards, and a sturdy rear carrier. The engine was unaltered, and transmission was via a Sturmer-Archer 3-speed gearbox.In February 1918 Motor Cycle reported[9] on a visit to Norton Motors. Mr Norton had stated that he expected three post-war models, the 3.5 hp 490cc TT with belt drive (for the 'speed merchant'), and two utility mounts, one with detuned TT engine, and the other being the Big Four for very heavy solo or sidecar work, both of these with three-speed Sturmey-Archer countershaft gearbox and all chain drive. It was also stated that he had been experimenting with aluminium pistons, and that Norton had produced a book of driving hints which also contained details of their Military and Empire models.
In May 1918 Norton stated in one of their adverts[10] that 'The ministry are taking the whole of our present output, but we have a waiting list' - this advert also uses the "Unapproachable Norton" phrase. Few Norton WD models appear in the For Sale column of The Motor Cycle after the war, suggesting they were shipped abroad, apparently one order going to the Russian Army [1]. The 1913-1917 Red Book[11] listing UK Motor, Marine and Aircraft production shows Norton dropped from a full range in 1916, to only the Military Big Four in 1917.
Inter-War Years
Norton resumed deliveries of civilian motorcycles in April 1919, with models aimed at motorcyclists who enjoyed the reliability and performance offered by long-stroke single-cylinder engines with separate gearboxes.Norton also resumed racing and in 1924 the Isle of Man Senior TT was the first win with a race average speed over 60 mph, rider Alec Bennett. Norton won this event ten times until they withdrew from racing in 1938.
J.L. Norton died in 1925 aged only 56, but he saw his motorcycles win the Senior and sidecar TTs in 1924,[12] specifically with the 500cc Model 18, Norton's first overhead valve single.[13]
Designed by Walter Moore, the Norton CS1 engine appeared in 1927, based closely on the ES2 pushrod engine and using many of its parts. Moore was hired away to NSU in 1930, after which Arthur Carroll designed an entirely new OHC engine destined to become the basis for all later OHC and DOHC Norton singles. (Moore's move to NSU prompted his former staff to quip NSU stood for "Norton Spares Used") The Norton racing legend began in the Thirties: Of the nine Isle of Man Senior TTs (500 cc) between 1931 and 1939, Norton won seven.[14]
Until 1934, Norton bought Sturmey-Archer gearboxes and clutches. When Sturmey discontinued production Norton bought the design rights and had them made by Burman, a manufacturer of proprietary gearboxes.
Second World War
Norton started making military motorcycles again in 1936 after a tender process in 1935 where a modified Norton 16H beat contenders. From 900 in 1936, to 2000 in 1937, Norton were ahead of the game as war loomed, and there was good reason in terms of spares and maintenance for the military to keep to the same model. Between 1937 and 1945 nearly a quarter (over 100,000) of all British military motorcycles were Nortons, basically the WD 16H (solo) and WD Big Four outfit with driven sidecar wheel.[2]Post war
The Isle of Man Senior TT successes continued after the war, with Nortons winning every year from 1947 to 1954.After the Second World War, Norton reverted to civilian motorcycle production, gradually increasing its range. A major addition in 1949 was the twin cylinder Model 7, known as the Norton Dominator, a pushrod 500 cc twin-cylinder machine designed by Bert Hopwood. Its chassis was derived from the ES2 single, with telescopic front and plunger rear suspension, and an updated version of the gearbox known as the "lay-down" box. More shapely mudguards and tanks completed the more modern styling to Nortons new premium model twin.
Norton also experimented with engine placement, and discovered that moving the engine slightly up/down, forward/back, or even right/left, could deliver a "sweet spot" in terms of handling. Motorcycle designers still use this method to fine-tune motorcycle handling.[16]
In 1951, the Norton Dominator was made available to export markets as the Model 88 with the Featherbed frame. Later, as production of this frame increased, it became a regular production model, and was made in variants for other models, including the OHV single-cylinder machines.
Manx Nortons also played a significant role in the development of post war car racing. At the end of 1950, the English national 500 cc regulations were adopted as the new Formula 3. The JAP Speedway engine had dominated the category initially but the Manx was capable of producing significantly more power and became the engine of choice. Many complete motorcycles were bought in order to strip the engine for 500 cc car racing, as Norton would not sell separate engines.
The racing successes were transferred to the street through cafe racers, some of which would use the featherbed frame with an engine from another manufacturer to make a hybrid machine with the best of both worlds. The most famous of these were Tritons - Triumph twin engines in a Norton featherbed frame.
-
Pre-unit Triumph engined Triton Café racer
AMC
1967 Norton Atlas
Main article: Associated Motorcycles
Despite, or perhaps because of, the racing successes Norton was in financial difficulty. Reynolds
could not make many of the highly desired Featherbed frames and
customers lost interest in buying machines with the older frames. In
1953 Norton sold out to Associated Motorcycles (AMC), who owned the brands AJS, Matchless, Francis-Barnett and James. In 1962 the Norton factory in Bracebridge Street, Birmingham was closed and production was moved to AMC's Woolwich factory in south-east London.Under AMC ownership a much improved version of the Norton gearbox was developed, to be used on all the larger models of AJS, Matchless and Norton. Again, the major changes were for improved gear selection. In September 1955, a 600 cc Dominator 99 was launched. The 1946 to 1953 Long Stroke Manx Norton was 79.6 mm × 100 mm (3.1 in × 3.9 in) initially SOHC, the DOHC engine becoming available to favoured racers in 1949. The Short Stroke model (1953 to 1962) had bore and stroke of 86 mm × 85.6 mm (3.4 in × 3.4 in). It used a dry sump 499 cc single-cylinder motor, with two valves operated by bevel drive, shaft driven twin overhead camshafts. Compression ratio was 11:1. It had an Amal GP carburettor, and a Lucas racing magneto. The 1962 500 cc Manx Nortons produced 50 bhp (37 kW) at 6,780rpm, weighed 142 kg (313 lb), and had a top speed of 209 km/h (130 mph).
In 1960, a new version of the road-going Featherbed frame was developed in which the upper frame rails were bent inwards to reduce the width between the rider's knees for greater comfort. The move was also to accommodate the shorter rider as the wide frame made it difficult to reach the ground. This frame is known as the "slimline" frame; the earlier frames then became known as the "wideline".
The last Manx Nortons were sold in 1963. Even though Norton had pulled out of Grand Prix racing in 1954, the race-shop at Bracebridge Street continued until 1962, and the Manx became a mainstay of privateer racing, and even today are highly sought after, commanding high prices.
On November 7, 1960 the first new 650cc Norton Manxman was launched for the American market only. By September 1961 the Norton 650SS appeared for the UK market, The 750cc (Atlas). By April 20, 1962 for the American market as they demanded more power, but the increases to the vertical twin engine's capacity caused a vibration problem at 5500 rpm. A 500cc vertical twin is smoother than a single-cylinder, but if the vertical twin's capacity is enlarged vibration increases. The 750 Norton Atlas proved too expensive and costs could not be reduced. Financial problems gathered.[17]
There was an export bike primarily for use as a desert racer, sold up until 1969 as the Norton P11,[18] AJS Model 33 and Matchless G15, which used the Norton Atlas engine in a modified Matchless G85CS scrambler frame with Norton wheels and front forks. This bike was reputed to vibrate less than the Featherbed frame model. AMC singles were also sold with Norton badging in this era.[19]
Also during this period Norton developed a family of three similar smaller-capacity twin cylinder machines: first the Norton Jubilee 250 and then the Navigator 350 and the Electra 400, which had an electric starter. These models were Norton's first use of unit construction. The engine was an entirely new design by Bert Hopwood and the frame and running gear were from the Francis-Barnett range, also owned by AMC. These machines had a reputation for poor reliability.[citation needed]
Norton-Villiers
Main article: Norton-Villiers
By the late 1960s, competition from Japanese manufacturers and a rapidly declining home market[citation needed] had driven the whole British motorcycle industry into decline. In 1966 AMC became insolvent and was reformed as Norton-Villiers, part of Manganese Bronze Holdings Ltd.The 750 Norton Atlas was noted for its vibration. Rather than change engines Norton decided to change the frame, and the isolastic-framed Norton Commando 750 was the result.
1973 850 Commando
The "Combat" engine was released in January 1972, with a twin roller bearing crank, 10:1 compression and developing 65 bhp (48 kW) at 6,500 rpm. Reliability immediately suffered, with frequent and early crank-shaft main-bearing failures, sometimes leading to broken crankshafts. Older engines had used one ball-bearing main bearing and one roller bearing main bearing but the Combat engine featured two roller bearings in a mistaken belief this would strengthen the bottom-end to cope with the higher power-output. Instead the resultant crank-bending caused the rollers to "dig-in" to the races, causing rapid failure. This fragility was particularly obvious when measured against the reliability of contemporary Japanese machines.[20] This problem was solved by specifying a heavier duty type of spherical roller bearing, of 'superblend' fame, later in the 1972 production year.
The Commando was offered in several different styles: the standard street model, a pseudo-scrambler with upswept pipes and the Interstate, packaged as a tourer. Electric start was introduced on the Mark III in 1974. Sales were respectable but the company declined financially and became insolvent in 1975.[14] In 1976 a Norton with a US-flag theme on the tank could be purchased for US$1,976.
Norton Villiers Triumph
1978 Commando Interstate Mk3
Main article: Norton Villiers Triumph
In 1972, BSA was also in financial trouble. It was given UK Government help on the condition that it merged with Norton-Villiers, and in 1973, the new Norton Villiers Triumph (NVT) was formed. The Triumph Motorcycles
name came from BSA's Triumph subsidiary. In April 1973 an 8.5:1
compression 828 cc "850" engine was released with German FAG SuperBlend
bearings. These, featuring slightly barrel-shaped rollers, had been
introduced on late model 750 cc engines to cure the Combat engine's
problems of crank-flex and the consequent digging-in to the
bearing-surface of the initial cylindrical bearing rollers. This model
produced 51 bhp (38 kW) at 6,250 rpm but the stated power does not give a
true picture of the engine performance because increased torque seemed
to make up for the reduced horsepower.[21]In 1974, the UK's outgoing Conservative government withdrew subsidies, but the incoming Labour government restored them after the General Election. Rationalisation of the factory sites to Wolverhampton and Birmingham (BSA's Small Heath site) caused industrial disputes at Triumph's Coventry site; Triumph would go on as a workers cooperative alone. Despite mounting losses, 1974 saw the release of the 828 Roadster, Mark 2 Hi Rider, JPN Replica (John Player Norton) and Mark 2a Interstate. In 1975, the range was down to just two models: the Mark 3 Interstate and the Roadster, but then the UK Government asked for a repayment of its loan and refused export credits, further damaging the company's ability to sell abroad. Production of the two models still made was ended and supplies dwindled.
1973 also saw the start of development on a new machine with a monocoque pressed steel frame, that also included a 500 cc twin, stepped piston engine[22] called the 'Wulf'. However, as the Norton Villiers Triumph company was again in serious financial problems, development of the 'Wulf' was dropped in favour of the rotary Wankel type engine inherited from BSA.
Wankel engine
In the 1980s, the company went through several incarnations – mainly because the name was popular and now owned by several parties. In liquidation from NVT the global rights were split between (at least) Norton UK, Germany, America and Rest of the World. MidWest acquired the rights for light aviation use, and at Staverton Airport the MidWest AE series was an aero engine developed from the twin-rotor engine.The brand was relaunched on an ambitious scale in Lichfield in 1988. The new models succeeded in racing – winning the Senior TT in 1992 – but they moved rather more slowly in the commercial market. The company had some success making the Wankel-engined Interpol 2 motorcycle for civilian and military police forces and the RAC. This led to a civilian model in 1987 called the Classic.
Subsequent Norton Wankels were water-cooled. The Commander was launched in 1988 and was followed by the Spondon-framed F1. This model was a de-tuned replica of Norton's RCW588 factory racing machines which won many short distance races, but had many reliability issues requiring frequent servicing i.e. changing the primary drive chain every 100 miles.
1988 saw a new team brought in to replace Brian Crighton's team, to try to improve the model and reduce some of its reliability issues. The team, headed by ex Honda-team manager Barry Symmons, Honda engineer Chris Mehew and chassis specialist Ron Williams, were tasked with producing a chassis that could be produced cheaply and an engine which would have a long term reliability. The chassis, designed by Ron Williams and made by Harris Products, was based on Yamaha's Delta box stamped panels. However in spite of many innovative solutions from Chris Mehew, the team's efforts to improve the reliability of the engine could not succeed to a commercially saleable level. The team quickly realized that placing an engine generating 1100 °C exhaust temperatures was not the item to place under a petrol tank.
The team's project - renamed the NRS 588 - did win the 1992 Isle of Man TT, ridden by Steve Hislop, as well as North West 200 and Ulster Grand Prix races ridden by Robert Dunlop. Whilst in Northern Ireland, the team met Professor Gordon Blair, one of the foremost automotive engineers from Queen's University Belfast. Prof Blair commented that the Japanese had abandoned development of the motorcycle variant of the Wankel engine on two main counts: 1. As the team had realized, there was just too much heat to be confined in a motorcycle chassis. 2. The pollution created by the engine burning both oil for lubrication and fuel for power was just too great to meet the impending pollution regulations without a large and expensive exhaust scrubbing system. In his TV Series on British Industry Sir John Harvey Jones commented that the company was governed more by heart than head and the Racing team were the only ones worth saving.
The F1 was succeeded by the restyled and slightly less expensive F1 Sport. Chief Executive Phillippe LeRoux attempted to diversify the company to a group with interests in property and leisure,[23] meanwhile supply of Norton Classic was being delayed by supply problems with petrol tanks and headlight shells.[citation needed]
At this point the UK Department of Trade and Industry started to investigate improprieties in the investments of financier Philippe LeRoux and his associates[24] following which LeRoux resigned his position as Chief Executive.[25]
In a move to manage an outstanding debt of ₤7 million, in 1991 David MacDonald was appointed Chief Executive at the behest of the Midland Bank. McDonald sold the company to the Canadian company Wildrose Ventures in 1993 for around half a million pounds.[26][27]
Head of Wildrose Ventures, Nelson Skalbania, reformed the company as Norton Motors (1993) Ltd., putting his daughter Rosanda in place as General Manager at the Shenstone site.[28] The new ownership attempted to reclaim from public exhibition premises and place for auction with Sothebys ten historic motorcycles, estimated at the time to be worth £50,000,[26] including a 1904 Triumph first exhibited in 1938, which had been variously distributed to National Motor Museum, Beaulieu, Science Museum, London and Coventry Transport Museum.
This proved controversial as the museums had assumed the loans had been made on a permanent basis, and former Chief Executive David MacDonald stated "Without doubt anything which existed before 1984 does not belong to the present company. The assets were simply not transferred[26][29]
Wildrose Ventures was ordered by the Alberta Stock Exchange to cease trading.[26][27]In 1994 ownership of the company reverted to Aquilini Investments as Skalbania was unable to repay the money he had borrowed to purchase the company. The Skalbania connection was reported as being severed by July of that year[30]
By 1996 the service side of the Shenstone site was closed and transferred to a small factory at Rugeley, Staffordshire. The focus of manufacture was moved to the manufacture of components for light aircraft engines based on the rotary design.
It was reported in 2005 that a group of former Norton employees built nine F1 Sport models from existing stocks of parts.[31]
-
Ron Haslam on a rotary-engined Norton RCW588 racer
The Donington Park revival
During the late 1990s, Kenny Dreer of Oregon evolved from restoring and upgrading Commandos to producing whole machines. He modernised the design and in the early 2000s went into series production with the 961 Commando, but then suspended operations in April 2006.
Norton Command 961 Sport in 2009
The new operation at Donington Park has gone into limited production producing a motorcycle based on the Kenny Dreer 961 Commando. The new motorcycle only shares the outline of the Dreer bike; all aspects of the motorcycle have been re-designed in order to move into production. An updated and revised version of the rotary machine developed in the 1990s is also being developed.
In January 2011, it was announced the highly regarded designer Pierre Terblanche had departed Piaggio / Moto Guzzi to join Norton.[35] In August 2011, UK minister Vince Cable announced that the Government was underwriting a £7.5 million bank loan to Norton, to promote secure cash flow for their export sales. Garner responded that this finance would allow Norton to double annual production from 500 to 1,000 machines.[36]
Donington Hall
Donington Hall
Norton Motorcycles purchased Donington Hall from British Airways for an undisclosed sum, and will vacate the current Norton factory at Donington Park, which has about 40 employees.[38] Shifting operations from Donington Park will be carried out in phases so as to not interfere with either production or distribution of Norton's bikes.[
V




Komentar
Posting Komentar